 What is Kurtosis
What is Kurtosis
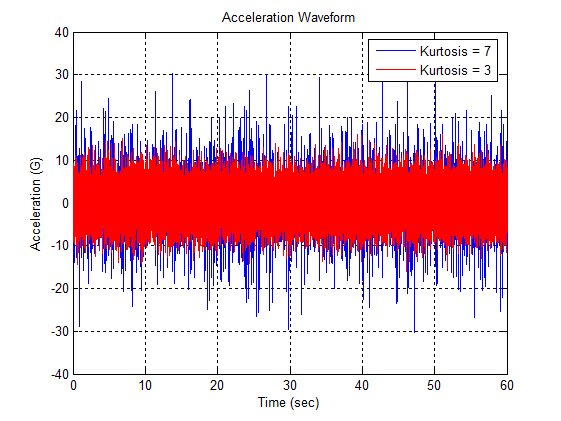 |  |
| Kurtosis is a statistical parameter that measures the peakedness or flatness of a vibration signal's distribution. The kurtosis value indicates the intensity of impulse peaks and sharp spikes in the signal. Interpreting Kurtosis
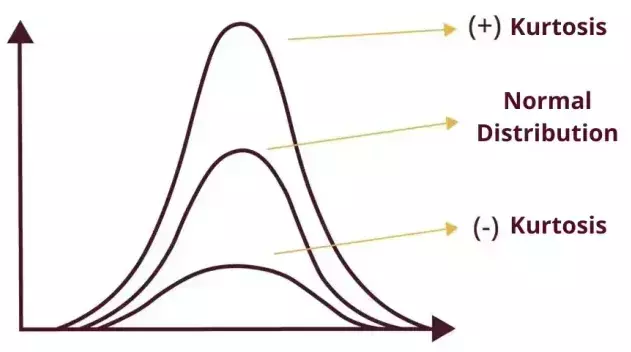
Graphical Analysis Kurtosis can also be interpreted from the distribution plot of vibration acceleration values:
Causes of High Kurtosis Values Kurtosis is particularly useful for detecting early-stage faults in components such as bearings and gearboxes. Abnormally high kurtosis values may indicate:
Conclusion Kurtosis is a valuable indicator for early fault detection in vibration analysis. It is particularly effective in identifying impact-related signals in bearings and gear systems. However, for accurate diagnosis, it should be used alongside other time and frequency domain parameters. | |

